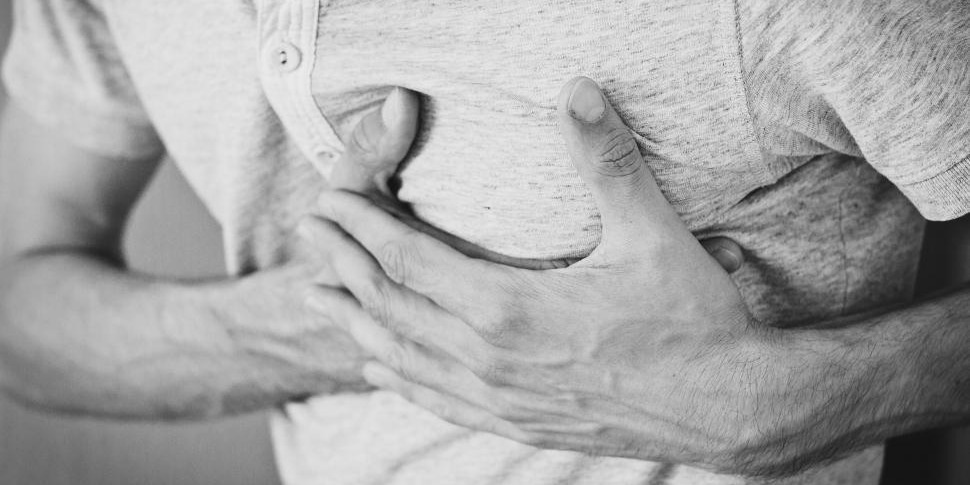
Myocardial infarction is also known as heart attack, which refers to a heart problem that causes the sudden stoppage of blood flow to the heart’s muscle. This is blocked by a blood clot in one of the coronary arteries; the coronaries provide oxygen and nutrients to the heart. Lack of timely medical treatment, a heart attack can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle and eventual demise.
In this extensive handbook, we are going to discuss the etiology, clinical picture, diagnostics, treatment, and prophylaxis of heart attack. We will discuss the risk factors, which undertake to plaque formation and accumulation in the coronary arteries and the resultant cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, we will analyze the numerous signs that signal a heart attack – those that are commonly overlooked or dismissed. Equipped with this knowledge, you will be able to identify those warning signals and seek medical attention as soon as you can.
The major cause of myocardial infarction is the plaque formation in the coronary arteries. This plaque is a build-up in cells made up of cholesterol and others that deposit themselves on the arterial walls, thus constricting the flow of blood. At times the plaque may rupture leading to formation of the blood clots that obstructs the artery and cuts off the blood supply to the heart muscles. It is the main cause of heart attacks.
Though the true etiology of myocardial infarction is unknown, there are several well- established risk factors that provide a propensity for plaque development and the consequent event.
Age and sex: Cardiovascular irs more common as age advance and that men are e at a higher risk than women. The danger begins to grow in men from 45 years old, while in women - from 50-year-old or after menopause.
Family history: If your family has a history of heart disease or heart attack, specifically during the early years of life, your risk is enhanced since it is based on shared gene factors.
Lifestyle choices: Poor health practices like smoking, non-activity, alcoholism, and drug abuse, among others, pose a high risk factor for heart diseases.
Underlying health conditions: Diabetes, obesity, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and presence of preeclampsia prior to pregnancy may add additional stress to the heart and contribute to plaque accumulation in the arteries.
By identifying these risk factors, people can engage in behavioural change to address their lifestyle, health issues and reduce the overall chance of a developing a heart attack.
Signalling the signs to identify a heart attack is essential to facilitate timely and appropriate medical intervention, which can spell a difference in life and death situations. Although this condition manifests through chest pain, it's also important to understand that the way people experience this problem differs and some people may have atypical or silent heart attacks that cause little to no chest pain.
Typical symptoms of a heart attack include:
Chest pain or discomfort: This can range from minimal irritation or heaviness to a crushing pain that is unbearable. The referred pain may affect the left arm, shoulder, neck, jaw, back, or abdomen.
Shortness of breath: When you can't catch your breath during light activity or rest, despite not engaging in intense physical activity.
Fatigue: Persistent, unexplained fatigue or an overwhelming, persistent exhaustion.
Nausea or stomach discomfort: Others might have stomach pains or a feeling of discomfort, which leads them to believe that all they have is indigestion or heartburn.
Heart palpitations: A feeling of palpitations in a fast or accelerated pattern.
Anxiety or a feeling of impending doom: Suspicion or intolerable fear.
Sweating: Prodigious sweating, which is sometimes referred to as cold or clammy.
Light-headedness or dizziness: Feeling weak or like you are about to faint.
It is also significant to point out that women and diabetics patients have weird symptoms sometimes. Women would have limitations of breath, tiredness, and nausea while provision of little or no chest pain is associated with people having diabetes.
In a case where you or any person close to you experience such symptoms, calling emergency services is incredibly important. Every second is vital in the treatment of a heart attack where early intervention has not only tremendously increased the chances of survival, but also helped to minimize the muscle damage of the heart.
It is critical to seek prompt medical attention if one is suspected of having a heart attack. Health care providers will perform a complete physical examination with assessment of vital signs and chest auscultation with the aid of a stethoscope. Heart performance of electrocardiogram (ECG) will be done to assess for any abnormality that points towards the heart attack.
Blood tests play an essential part in the diagnosis of a heart attack since they allow to establish the presence of some markers that signal damage to heart muscle. They are done multiple times over time to monitor the progress of the disease. The supplementary diagnostic methods, including coronary angiography, echocardiography, stress testing or heart CT scan are taken into account to estimate the levesl of blockages and monitor the heart functionality.
The second step is to have immediate treatment for a heart attack that is to have treatment that will increase the blood flow to the affected area of the heart muscle so as to minimize the damage or effects caused.
Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen is provided in order to increase the concentration of oxygen in the blood and to reduce cardiac load.
Medications: The treatment to prevent further clot formation is anti-clotting meds, including aspirin. Nitroglycerin can serve to relax blood vessels, thereby increasing the flow of blood. Breaking the blood clots is done using thrombolytic medications in case of emergency.
Angioplasty and stenting: Percutaneous coronary intervention or PCI is a minimally invasive procedure to open blocked coronary arteries. It entails the placement of a catheter with a balloon at the end of it inside the blocked artery and inflating the balloon in order to widen the artery.
A stent, a mesh tube made of metal, may be placed to prop the artery open and prevent re blockage.
In other instances, emergency maneuvers like coronary artery bypass grafting (CAGB) may become inevitable. In CABG, blood to the myocardium is redirected around the obstruction by generating a bypass using a blood vessel from another part of the body.
Following a myocardial infarction, appropriate recovery and long-term management are vital to prevention of further cardiovascular events. People will be well-educated on how to alter their lifestyles, how to diligently follow medication prescriptions, and aftercare.
Medication management: Post-Heart attack, patients may receive certain prescriptions to combat the underlying condition, to reverse high cholesterol, to manage high blood pressure, and to prevent blood clots. It is necessary to comply with the prescribed medicines and visit the doctor regularly.
Cardiac rehabilitation: Cardiac rehab program can be a foster towards recovery. These programs offer structured exercise, heart healthy advice and encouragement for emotional sustainability.
Heart-healthy lifestyle: Implementing dietary measures for heart-healthy, regular exercise, a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and stress management are important aspects of long-term management and prevention.
Emotional well-being: Emotional strain is often high after a heart attack. People can manage stress through seeking support from healthcare providers, joining support groups and practicing relaxation techniques that promote emotional wellness.
In this regard, preventing further heart attacks is of great significance for those who have undergone a heart attack.
Regular check-ups: Regular consultations with a primary care provider could enable evaluations of blood pressure, cholesterol, and other possibly associated risk factors. These factors can be detected and controlled early which significantly reduces the incidence of heart attack in future.
Healthy lifestyle choices: Regular exercise, healthy diet, controlled alcohol use and non-use of tobacco are some of the most important ways to prevent further heart attacks.
Medication adherence: Timely adherence to the prescribed medications is of importance to management of the underlying conditions and boosting prevention of further cardiovascular cases.
Stress management: This can be mitigated by practicing stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing, and fun that help lower the possibility of a heart attack in the future.
The road to recovery from a heart attack involves both physical and mental healing. Though the outcome of a heart attack depends on individual capacity, persons, with proper medical assistance usually recover and able to start normal life. You need to listen to your body and pace yourself according to the advice that your medical team gives about consuming food.
Remember yourself that you are not abandon on the road. The support groups for the people with heart disease may offer a supportive and understanding network. Peers sharing their feelings and actions during recovery can prove to be priceless in this process of recovery.
One of the adverse medical complications is myocardial infarction, commonly known as the heart attack, which is a life-threatening condition. By knowing the causes of heart attack, identifying the signs, getting medical care quickly and starting a heart-healthy life, people can slash their probability of experiencing a heart attack. Taking control of your health, complying with the guidance of the doctor, and obtaining emotional support will make you stronger and achieve a healthy heart life.
Disclaimer: For information only and not as medical recommendation. No matter the condition always make sure you seek diagnosis and treatment procedures from a trained health professional.